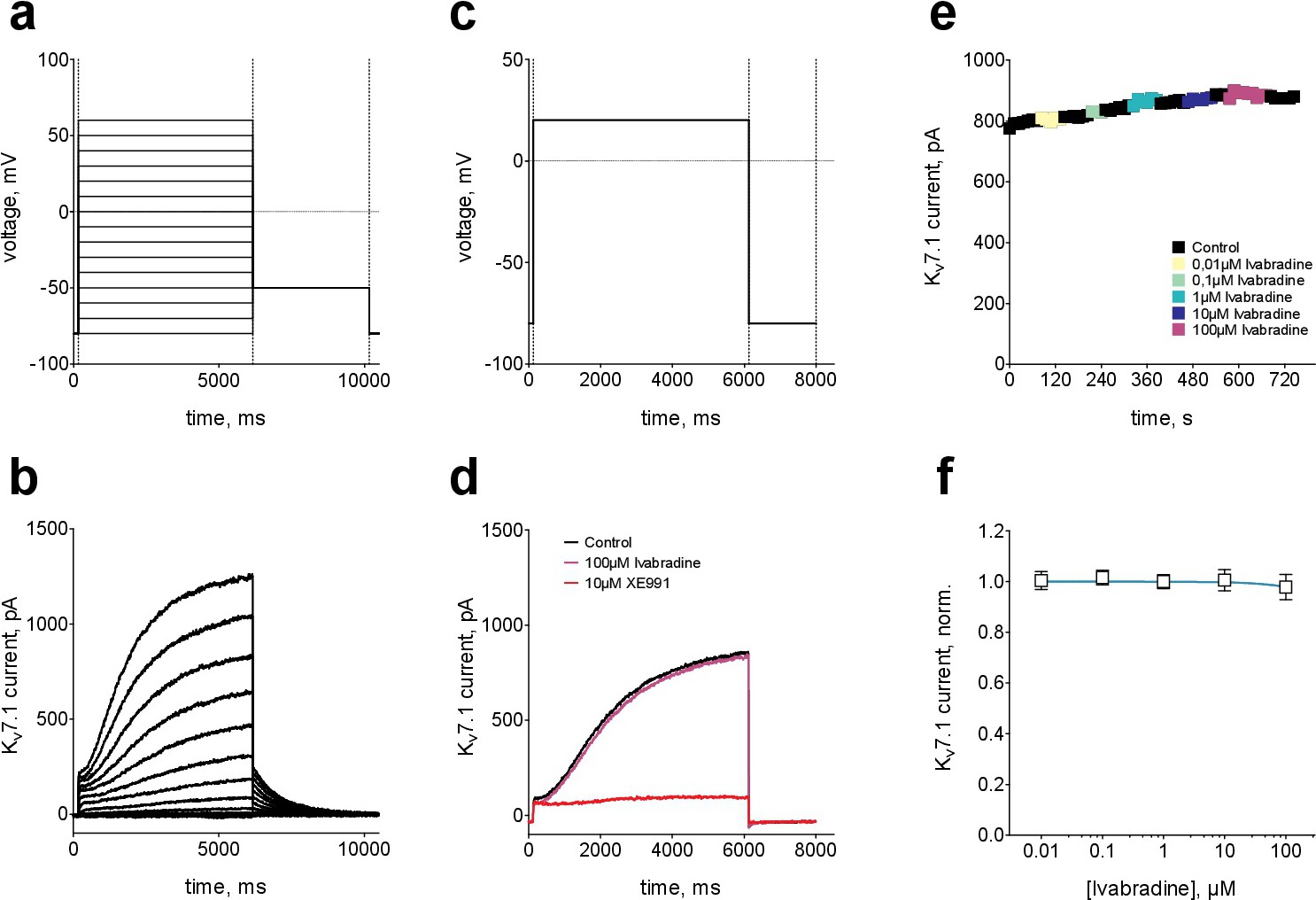
Fig. 2. Effect of ivabradine on heterologously expressed human Kv7.1 channels. (a) Voltage-clamp protocol to derive current voltage relationships. (b) Typical outward potassium currents as elicited by the voltage-clamp protocol shown in (a) for recombinant Kv7.1 channels expressed in tsA-201 cells. (c) A voltage-step to +20 mV was applied every 12 s to activate Kv7.1 channels. (d) Typical outward potassium currents for the voltage-clamp protocol shown in (c) under control conditions and in the presence of 10 and 100 ÁM of ivabradine. The peak of Kv7.1 current amplitude at the end of the +20 mV voltage-step was monitored to test for the effect of different ivabradine concentrations. A saturating concentration (10 ÁM) of XE-991, a selective inhbitor of Kv7.1 channels, was applied at the end in some experiments. (e) Kv7.1 current amplitude as elicited by the voltage-clamp protocol in (c, d) under control conditions and in the presence of ascending concentrations of ivabradine. (f) Summary of normalized steady-state Kv7.1 current amplitudes (mean +- SEM, n = 7) for all ivabradine concentrations tested. No significant current inhibitions was observed for ivabradine concentrations up to 100 ÁM.